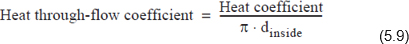Pipe Types
With the dialog Pipe Type a high-performance possibility is available to the user to reduce the number of repeating inputs for pipes by the definition of own pipe classes.
Class – Name of the pipe class.
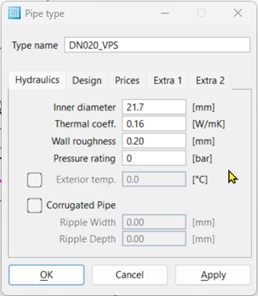
Hydraulics Tab
- Inside diameter – Inside diameter of the pipe class. The numerical value is relevant for hydraulic calculation.
- Heat coefficient – The
heat coefficient indicated the specific heat losses of the piping and enters
thermal calculation as heat transition coefficient.
- The heat transition coefficient is determined from the heat coefficient by division with the piping extent related to the inside diameter.
- The thermal calculation then takes place in accordance with Piping.
- Wall roughness – Surface roughness of the piping. This value is needed for the calculation of the pressure loss with the Colebrook White formula.
- Pressure rating – Pressure rating of the piping (max. permissible operating pressure).
- Retention correction – Correction factor for the retention time, to correct due to the storage effect in piping wall and isolation during the heating/cooling in the pipe. The value usually lies between 1 and 1.2 (default value = 1).
- Ambient temperature – Optional information of the ambient temperature for the heat loss calculation of the pipe. The default becomes effective if no individual exterior temperature is defined for pipes.
- Corrugated pipe –
Designates the pipe class as corrugated pipe and enables the input of
additional parameters for the description of corrugated pipe geometry. The
geometry details are to be taken from the manufacturer’s data sheet.
- Calculation takes place in accordance with worksheet FW 440-2 – [17].
- Groove distance – The distance between the high points of two grooves next to each other, in the direction of the piping axle.
- Groove depth – The distance between high and low point of a wave.
Design Tab
- Use for design – If this switch is pressed, the pipe class is available for design calculations. Otherwise the pipe class is not considered with design calculations and is not suggested for use.
- Max. spec. pressure loss – Maximum specific pressure loss for the pipe class.
- Max. velocity – Maximum velocity for the pipe class.
⚠ If these values for max. spec. flow rate are set, i.e., the numerical values are not equal to zero, you overwrite the global default from the network calculation.
See in the network calculation dialog Design Tab.
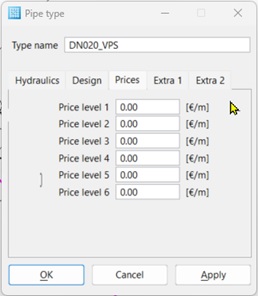
Prices Tab
Price level – With the price level, a specific moving price is assigned to the pipe class as a function of the moving conditions. The categories 1 to 6 are available across the application and can be filled according to your own needs.
The price indicated here together with the price stage selected in the pipes which of the 6 numerical values is to be used for a pipe for capital outlay calculation.
Extra 1 and Extra 2 Tab
Additional information – Under this point of dialog further specifications of the pipe class are possible regarding thermal insulation, supplier, material, order no., leakage detection, nominal diameter, shroud diameter, specific piping weight and outside diameter. These details are only for information and have no influence on network calculation.